Motivation
Motivation cycle:
- Needs creates behaviour to reach goals
- Goals creates new needs
Process vs. Content Two types of motivation theories
|
Content:
- Static
- Empasis on what motivates
- Concern with individual needs and goals
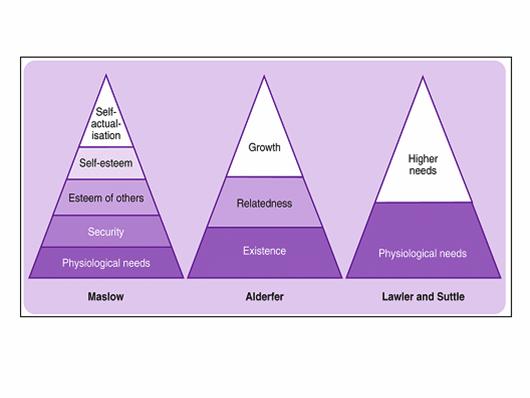
- Herzberg, Maslow, Aldefer, McClelland
|
Process:
- Dynamic
- Emphasis on the process of motivation
- Concern with how motivation occurs
- Vroom, Porter & Lawler, Adams, Locke, Heider, Kelley
|
McClelland’s Theory of Needs
- Need for achievement - The drive to excel, to achieve in relation to a set of standards, and to strive to succeed.
Want responsibility, feedback and some degree of risk
- Need for power - The need to make others behave in a way they would not have behaved otherwise
- Need for affiliation - The desire for friendly and close interpersonal relationships
About McClelland’s Theory
- High achievers are not necessarily good managers
- People driven by affiliation alone make quite weak managers.
- Affiliation and power together are closely related to managerial success
Herzberg’s satisfiers and dissatisfiers
|
Hygiene factors (extrinsic):
- Company policy
- Status/promotion
- Salary
- Job security
- Etc.
|
Motivators (intrinsic):
- Sense of achievements
- Recognition
- Resposibility
- Personal growth
- The work itself
- Etc.
|
Hackman and Oldman´s work design model
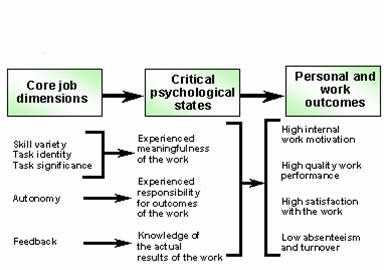
How do you implement it?
- Combine tasks
- Let people work in teams
- Empower
- Open feedback channels
McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y
- Two distinct views of people:
- Negative (Theory X) (lower needs)
- Positive (Theory Y) (higher needs)
- Managers view employees based on a group of assumptions
- Based on these assumptions, managers tend to mold their behavior toward employees
|
Theory X Workers:
- Dislike work
- Must be threatened with punishment
- Avoid responsibilities
- Seek formal direction
- Require security
- Little ambition
|
Theory Y Workers:
- View work as natural
- Self-directed
- Exercise self-control
- Accept responsibility
- Seek responsibility
- Make innovative decisions
|
Process vs. Content Two types of motivation theories
|
Content:
- Static
- Empasis on what motivates
- Concern with individual needs and goals
- Herzberg, Maslow, Aldefer, McClelland
|
Process:
- Dynamic
- Emphasis on the process of motivation
- Concern with how motivation occurs
- Vroom, Porter & Lawler, Adams, Locke, Heider, Kelley
|
Goal-Setting Theory
- Goals are a potent motivating force
- Specific goals lead to increased performance
- Difficult goals, when accepted, result in higher output than easy goals
- Participation in setting the goals might motivate further
- Set goals only, not the route to achieve it
FRAME
Goals should be:
- Few
- Realistic
- Agreed
- Measured
- Explicit
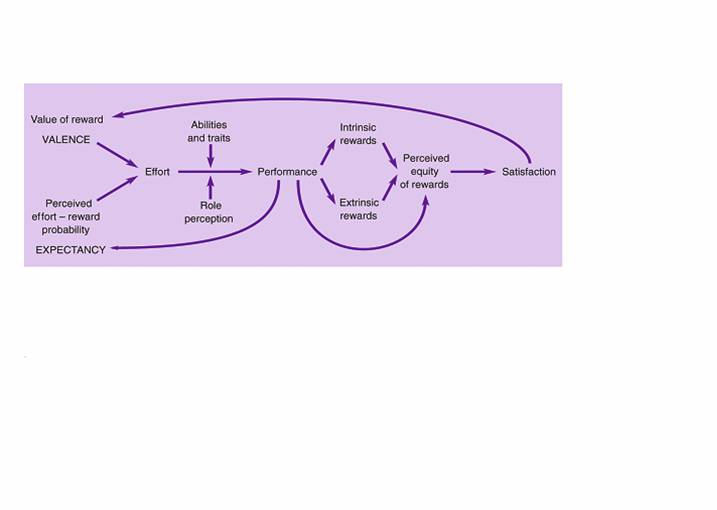
Expectancy theory (Vroom and others)
- Motivation = expectation*attr.
- Strength of a tendency to act in a certain way depends on
- Strength of expectation that the act will be followed by a given outcome
- Attractiveness of that outcome to the individual
- Attractiveness - The importance the individual places on the potential outcome or reward that can be achieved
on the job; considers the unsatisfied needs of the individual
- Performance-reward linkage - The degree to which the individual believes that performing at a particular level
will lead to the attainment of a desired outcome
- Effort-performance linkage - The probability perceived by the individual that exerting a given amount of effort
will lead to performance
Porter and Lawler’s expectancy model
Equity Theory (Adams and others)
- Employees weigh what they put into a job situation (input) against what they get from it (outcome)
- Then they compare their input-outcome ratio with the input-outcome ratio of relevant others
- If they perceive their ratio to be equal to that of relevant others, a state of equity exists otherwise inequity
Employee recognition programs
- Using multiple sources to reward behavoiur and recognize publicly both individual and group accomplishment
- Rewarding behavior with recognition immediately leads to its repetition
- To maximize motivation potential, publicly communicate who and why is being recognized
- Recognizing employee’s superior performance often costs little
Employee involvement
- A participative process that uses the entire capacity of employees related to decisions that affect them is
designed to encourage increased commitment to the organization's success
- Involve workers in decisions that will affect them
- Increase their autonomy and control over their work lives
- Include techniques with a common core
- Employee participation
- Participative management
- Workplace democracy
- Empowerment
- Employee ownership
Variable-pay programs
Forms of compensation where a portion of an employee’s pay is based on the measure of performance either of the
individual, the organization, or both
Four widely used variable-pay programs
- Piece-rate wages - fixed sum for each unit completed
- Bonuses - a percent of annual pay based on company earnings
- Profit sharing - based on a formula designed around company’s profitability
- Gainsharing - formula-based group incentive plan for improvements in productivity
Skill-based pay
Pay levels based on how many skills employees have or how many jobs they can do
Advantages:
- Attractive due to flexibility for management
- Encourages employees to acquire a range of skills
- Facilitates communication and understanding of others’ jobs
- Meets needs of ambitious employees without a promotion in job title
Disadvantages:
- Topping out - learning all the skills
- Skills might become obsolete
- Do not address level of performance
Belbin’s 9 team roles
1 Implementer
2 Plant
3 Coordinator
5 Shaper
6 Specialist
7 Teamworker
8 Monitor/evaluator
10 Completer/finisher
12 Resource investigator
<


